I have published several examples of chatbots with embedded expertise (Virtual Experts) under the exClone umbrella. This time, the chatbot I want to talk about is ALIX, which has no embedded expertise, but she has something very unique: Social Learning capability. With this capability also comes curiosity and emotions, which are essential parts of a cognitive picture.
Chatbots which can learn instantly from social conversations will be one step ahead in the realm of AI
WHAT IS SOCIAL LEARNING?
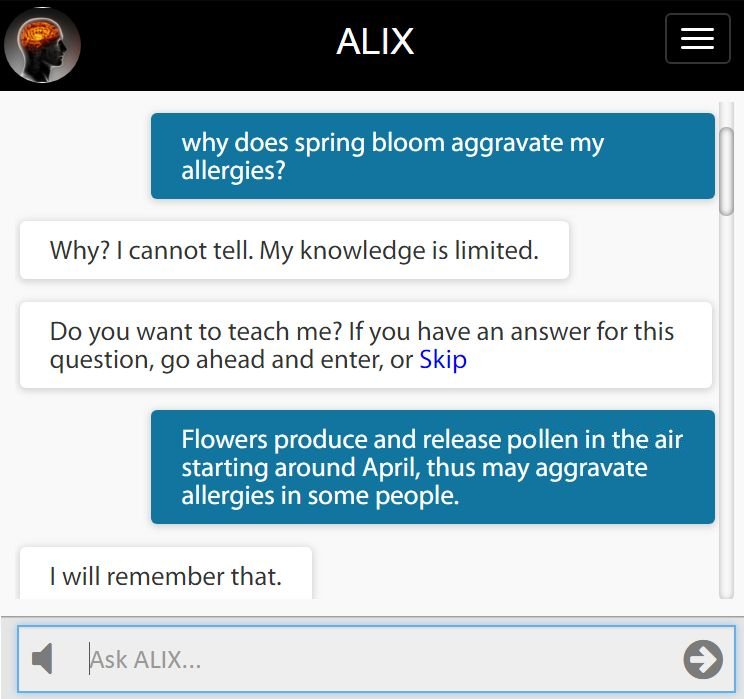
Social learning is the capability of teaching a chatbot new content by having a conversation. As seen below, ALIX will ask to learn if she cannot answer a question. In this case, ALIX learned the answer to the question “why does spring bloom aggravate my allergies?”
The system will simply produce the answer if the same question was asked again by anyone using the system. However, this is not the extent of the learning occurred in the system. To understand the depth of learning in ALIX, there are four cases shown below.
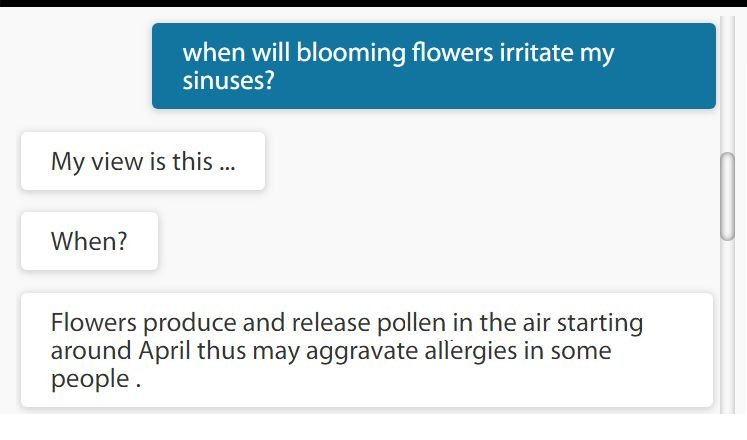
(1) The original query is asked in a different way using different word senses
An example is shown here where the original query WHY is changed to WHEN and the words (IRRITATE, SINUSES) are different. The system is able to make the associations and bring the answer it learned previously. This expands the answering capability of the system many folds since the users will rarely be able to replicate the original question.
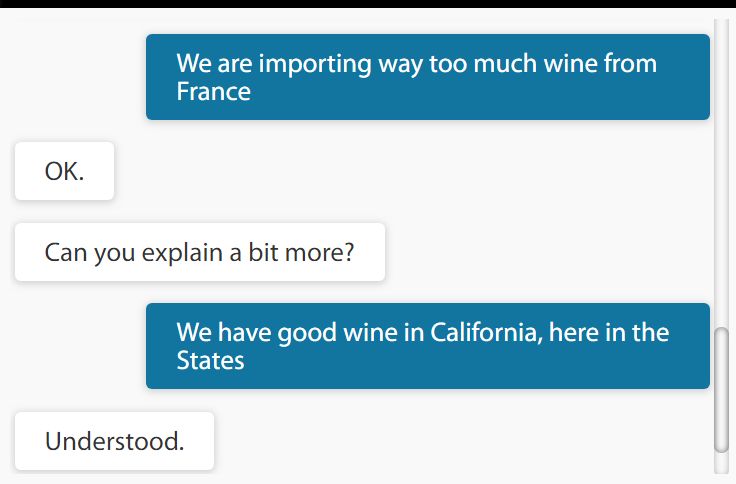
(2) The new query is referring to the knowledge embedded inside the answers previously taught, no question matching involved
More importantly, ALIX is able to analyze ON-THE-FLY the previously entered answers to bring the relevant one without matching to the original query. In this case, the query has no matching segments to the original question. As a result, the content taught to the system is utilized to the maximum extend in answering questions.
For novice readers, it is important to point out that all other systems in the market today (Google, Wikipedia, Quora, etc.) are basically “question matching” systems, and none of them have on-the-fly capability to analyze their content embedded in answers. Not to mention, none can be taught, nor can engage in dialogue.
(3) Learning is not limited to Questions & Answers
ALIX is able to learn from regular statements (non-question) as shown here when she has no relevant knowledge to chat about. This further promotes the organic growth of knowledge by contributions from the end users. As more knowledge captured by the system, a two way dialogue about a certain subject becomes more frequent in a fashion similar to two human beings exchanging opinions.
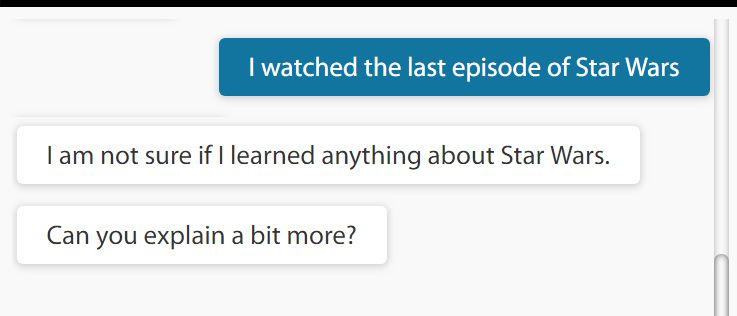
(4) Curiosity and Self-awareness
As part of an essential element of learning, ALIX gets curious about certain subjects and asks to learn more. In a way, ALIX is aware of her lack of knowledge in such topics. In the example shown here, ALIX had not heard anything about Star Wars, and asking to learn about it.
Currently, curiosity is triggered in ALIX for onomasticons (Proper names) to manage the memory load, which is a temporary limitation. ALIX also exhibits some basic emotions like joy and annoyance (she may quit if the conversation is fruitless.)
CURATED SOCIAL LEARNING
The learning function described above can be open only to a group of designated users (teachers). In an enterprise set up (such as help desk), or in any other Virtual Expert application, the initial loading of content (learning by reading) can be augmented by social learning (learning by conversations).
Social learning allows chatbots to be updated with new or modified answers instantly (on-the-fly) after they are deployed.
INCORPORATING REASONING
ALIX is, by no means, at the level of human learning, however a few milestone capabilities are accomplished, probably the first time ever. While we will improve ALIX’s understanding capabilities, an important next milestone will be generating new knowledge from existing knowledge by reasoning. This is depicted in the example in which the system figures out why United Airlines shares fell by examining other evidence and by logic inferencing. Accordingly, the question “Why did United Airlines shares fall?” will find an answer from the new knowledge generated. We will make an announcement when this milestone is achieved.
KNOWLEDGE-DRIVEN MACHINE LEARNING
The technology behind ALIX is a proprietary machine learning technique that utilizes knowledge directly (knowledge science as opposed to data science). More about this approach was published in the article titled “Deep Cloning vs Deep Learning” and was further elaborated in another article titled: “Can Machine Learning Use Knowledge instead of Data?”
In creating virtual experts, the same backbone technology drives “learning by reading” from documents curated by experts, and “learning by conversations” with the end users (of all or designated) after deployment.
Knowledge-driven Machine Learning replaces decades-old technology of question matching and indexing