Category Archives: Uncategorized
Artificial Intelligence to Help Fight Pandemics like the Coronavirus
A Forbes article published last week reported that Chinese chatbots (WeChat and Alipay) were used to suppress the spread of the Covid-19 virus. Although the chatbots did something unacceptable in Western societies (i.e., using the assigned color codes like red, green, or yellow to indicate individuals’ freedom level for travel and social activities), they produced effective results in a short period. And the article mentioned nine other ways that AI can be useful in such circumstances.
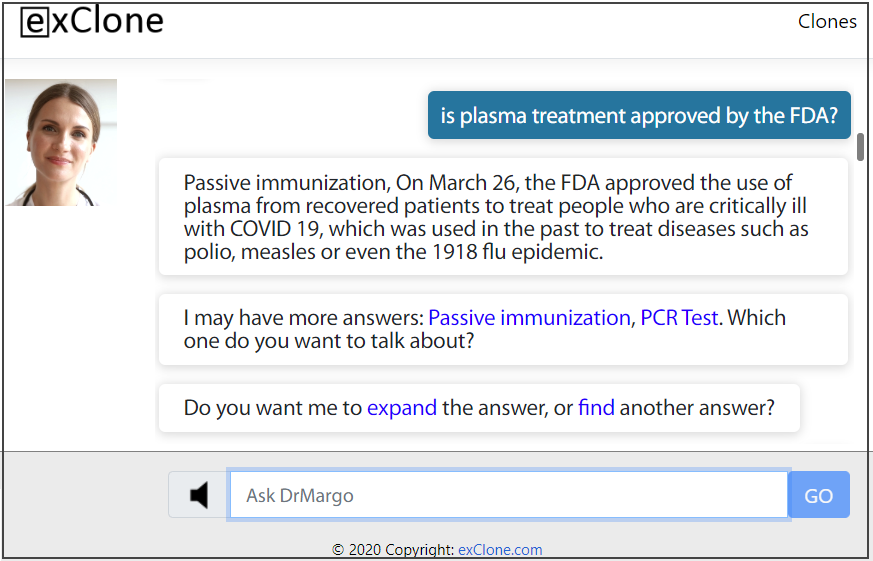
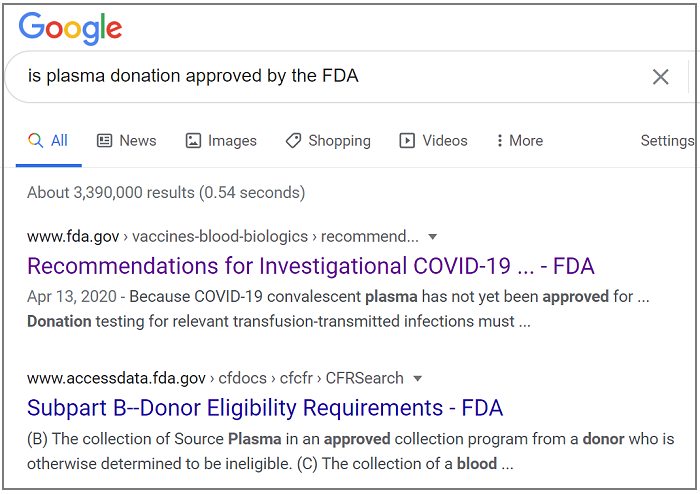
When it comes to disseminating credible, useful, and unique information, chatbot technologies can deliver valuable insights promptly and accurately. For example, the question “Is plasma donation approved by the FDA?” produces a clear answer by exClone’s virtual expert, Dr. Margo, compared to Google search results.
On the other hand, asking Google the same questions produced contradictory results written in a language that is not easy to understand (April 26, 2020, New York.)
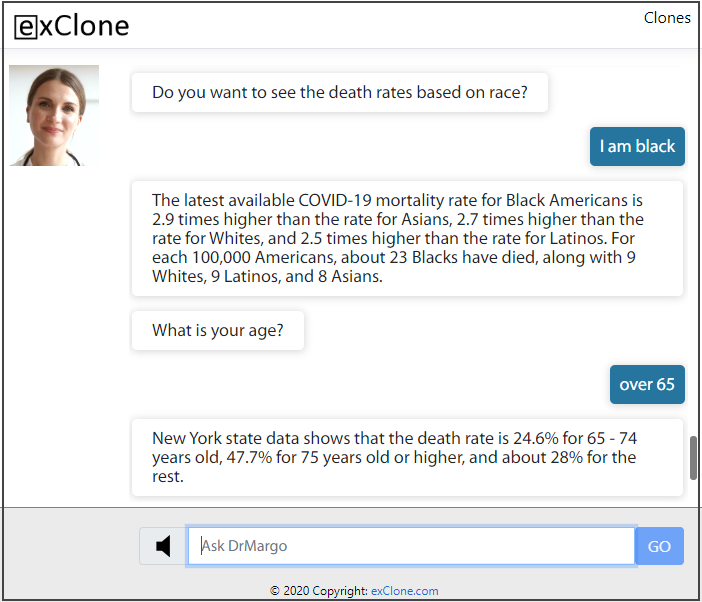
The virtual expert technology delivered by exClone does not only produce more precise answers to single-step questions, but also engages the user in a multi-step dialogue investigation, very similar to how a human expert would deliver advice. The important point here is the capability of the computer to ask the user questions to provide better answers as shown in the example below.
Google, Alexa, or other similar assistants do not ask the user questions for a more refined answer. This is the fundamental difference between the exClone’s dialogue technology (based on AI) versus short cut coding efforts devoid of AI.
exClone’s Dr Margo is a virtual expert that encapsulates knowledge from credible sources (curated by human experts) then disseminates accurate answers in a multi-step, human-like dialogue. The human expert can continue teaching the system after deployment by just talking to it.
The BETA version of Dr. Margo is available via mobile apps (with voice interaction like Alexa) or by the Web app at this link.
Enterprise IQ and Virtual Experts
In its simplest form, the Enterprise IQ concept assumes an imaginary brain of an organization where all know-how and expertise are gathered, then distributed at maximum scale so that the workers can utilize it rapidly and effectively. The AI application of Virtual Experts helps this vision to become a reality as summarized below.
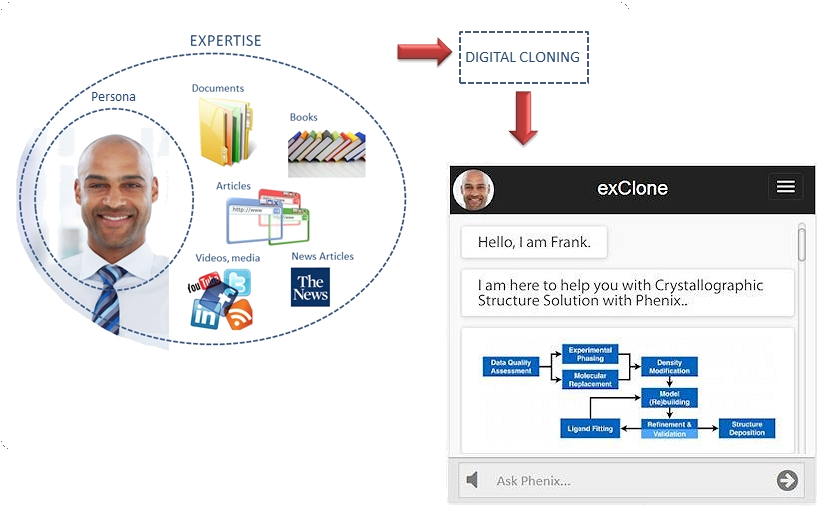
Cloning Experts to yield Virtual Expert
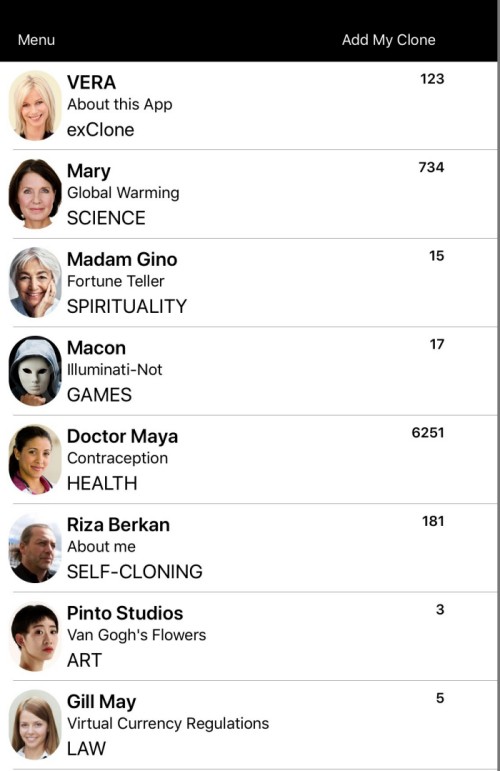
Cloning experts refers to capturing the knowledge of an expert and being able to apply it when appropriate. The curation of the expertise may include documents, reference materials (such as books), articles, news feeds, conversation logs, and media sources like videos. The curator can be an expert person, or a group of experts. Personal choices and dialogue behavior can also be adjusted. The expertise captured by digital cloning is delivered to the end user by a conversational (chatbot) interface. An example is shown below for the particular expertise of Crystallography.
Teaching the virtual expert can continue after the deployment by allowing designated users to teach it via conversations. Such a cloning process makes the in-house expertise captured, preserved, and protected in case of experts leaving the enterprise. An enterprise can launch as many virtual experts as necessary to help its workers and/or customers, or launch a master virtual expert to handle all the subjects.
Expertise Accessible by the Masses
The most important function of a virtual expert is its scalability where 1000s of people (workers and/or customers) can converse with it simultaneously. The value is realized when critical questions are answered instantly without the need to talk to the human expert. The only alternative to virtual experts, today, is going through document stockpiles to find answers manually (or by rudimentary search engines which are notoriously ineffective).
Being able to access expert knowledge instantly via natural language dialogue is an enhancement to Enterprise IQ and improves bottom line.
__________________________________________________________
This article is brought to you by exClone.
Join CHATBOTS group in linkedin.
You can follow exClone in Facebook, and in LinkedIn.
Request a Demo from exClone
Download exClone App (iOS) — Ecosystem of virtual experts (beta)
Download exClone App (Android) — Ecosystem of virtual experts (beta)
___________________________________________________________
#AI #Experts #EnterpriseIQ #Virtualexperts #Voiceassistants #practicalAI #chatbot #chatbots #artificialintelligence #ConversationalAI #Virtualassistants #bots #machinelearning #NLP #DL #deeplearning
Originally published at https://www.linkedin.com.
Cortana Out exClone In
A recent article reports ” Come the end of January, it appears the Cortana app’s getting booted to the Microsoft assistant graveyard. At least poor Clippy will have some company now. That’s according to a support article Microsoft posted to several regional markets this week.” After Siri becoming a laughing stock, Cortana’s departure is not surprising. These “can-do-it-all” voice assistants are simply not delivering the AI promise. Their utility have been questioned with the exception of Alexa due to its clever commercial use attached to playing songs.
Instead of “can-do-it-all”single voice assistant, exClone has just released an app (experimental) that is an ecosystem of virtual experts (chatbots). Starting with 8 examples, each virtual expert is focused on a different subject as designed by its owner. Contributors to the ecosystem can be anyone or any organization who can clone themselves into a virtual expert via exClone’s platform. The cloning process requires nothing but documents (Word or PDF) that contain the knowledge of potential conversation with the visitors. Contrary to “can-do-it-all” attitude, this environment offers number of virtual experts (conversational agents with voice). Once the ecosystem reaches its maturity, finding the relevant virtual expert will be easy via a category search function (i.e. HEALTH, LAW, ART, etc.)
Download the App
Please download the exClone app from the links below. If you already have it, you should update it with the latest version. Please bear in mind, this is an BETA test.
New clones/virtual experts are added regularly without the need for you to update the app. Notifications will highlight the newly added clones and their content changes.
Practical AI: Deep Learning Costs Reduced 100 times via Instant Learning Yielding Industry Level Performance
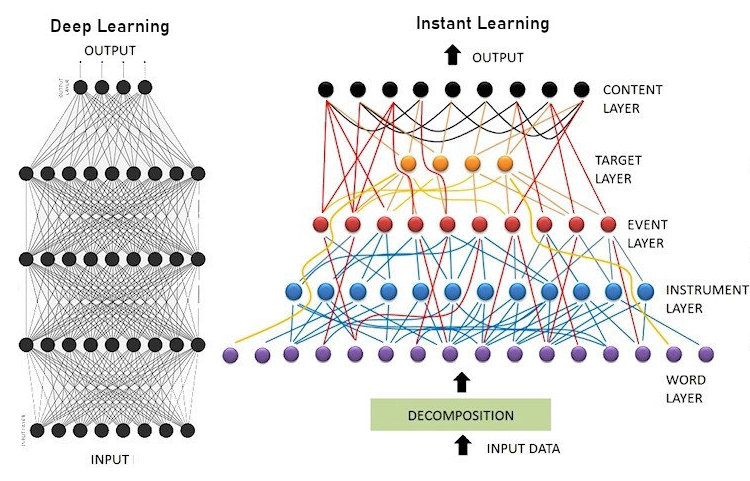
In reference to my earlier post about the exClone Case Study reported by Forbes, the future of conversational AI signals a shift from data-driven, expensive, and lengthily methods to knowledge-driven, affordable, and fast methods. In short, it boils down to Deep Learning (DL) versus Instant Learning (or its derivatives).
The two different approaches are summarized in the diagram below.
Practical AI, the right side of the diagram above, uses the existing knowledge on linguistics, ontological semantics, psychology, neuro-sciences, and other cognitive sciences. The resulting hybrid method reduces the load of a machine learning algorithm, turning it into a mere knowledge absorption step from documents (similar to how we read and learn). These documents are about the subject matter of which the conversational system talks about, but nothing more. Simplicity and speed give it the name, instant learning.
Conventional AI, the left side of the diagram, dismisses most (if not all) the existing knowledge, and assumes to solve everything by data crunching. The required data set is assumed to contain examples of all cognitive skills in language processing which is an overly optimistic (if not impossible) expectation.
The Cost Issue
When you have to acquire, validate, and process data, the costs can sky rocket. In my earlier article, the example of Morgan Stanley’s AskResearch system, which is reported to bring answers to somewhat mediocre questions like “What is Morgan Stanley’s standpoint on gold?”, took 1 year to train the system. Obviously, the costs associated with such a process, and data services, would wind up in 7 figures. Not to mention the cost of the required staffing, and the repeating cost cycle in every correction attempt.
In contrast, the practical AI example of exClone’s deployment of Virtual Experts for enterprises can cost 100 or 1000 times less. Because, no data is utilized, no AI staff is required, no coding is necessary, no long training cycles are endured. The only required effort centers around editorial, document management, and curation.
If engineering means finding the most practical and affordable solution, then the sole DL application to NLP may be the worst engineered systems to date!
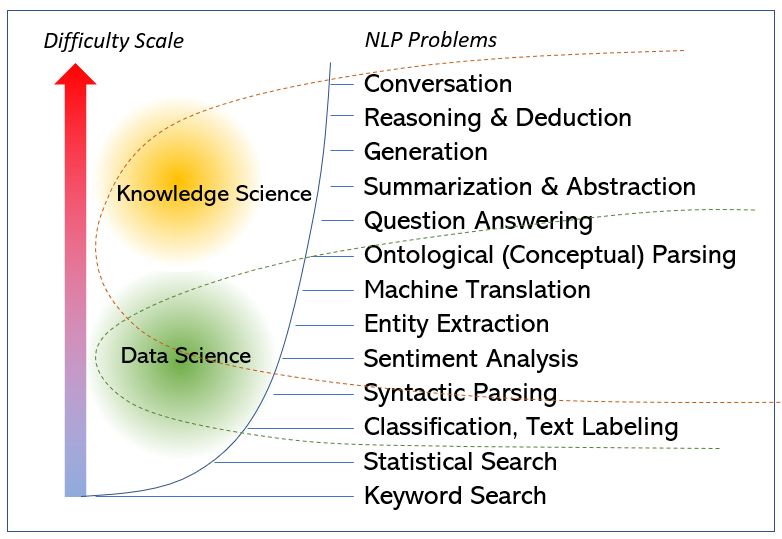
The Difficulty Scale of NLP
One common problem I see in the DL community is the unawareness of the difficulties of different NLP problems which reminds me of the saying “if the only tool is a hammer…” I made a conceptual scale as shown in the diagram below. Some may argue the ranking of few items. Nevertheless, the exponential nature of the complexity involved in these different problems is indisputable. For example, if your problem at hand is Text Labeling, you are light years away from handling Abstraction. Accordingly, if a DL approach proves successful in the former, it does not mean its readiness in the latter. The differences are huge.
More drastically, data-driven methods have inherent limitations to handle higher level NLP problems no matter the size of the corpus. At the lower end of the scale, most DL applications can be duplicated by statistical linguistics (such as in sentiment analysis) which begs the question “how much better is the conventional AI?”
Conclusion
Data is expensive and risky. Data driven methods make sense to attack problems of high level complexity where (1) the underlying principles are not well known, such is in stock market analysis, or (2) the complexity arises from multi-body nature of the problems, such as in atmospheric modeling or image processing. Applying DL to NLP is treating NLP like atmospheric modeling. More sensible approach is to utilize available knowledge at its maximum, then apply machine learning for the remainder of the problem. This requires innovation of hybrid systems. exClone’s instant learning technology is one good example, however more hybrid solutions are expected to emerge in the near future.
——————————————-
This article is brought to you by exClone, a Virtual Expert & Chatbot technology provider via its proprietary Instant Learning technology.
- Request for a demo at exClone.com
- Join CHATBOTS group in linkedIn.
- You can follow exClone in Facebook, and in LinkedIn.
#AI #ArtificialIntelligence #virtualexperts #chatbots #conversationalAI #ML #DL #deeplearning #Machinelearning #exclone #NLP #humandialoguetheory #instantlearning #virtualreality #VR #StanleyMorgan
exClone Launches Virtual Experts at Black & Veatch to Enhance Knowledge Utilization by Artificial Intelligence
NEW YORK–(BUSINESS WIRE)–Today, exClone Inc. announced the launch of its AI-based virtual experts at Black & Veatch as an enhancement to enterprise knowledge capture, utilization, communication, and search functionality.
exClone’s virtual experts open a new, unprecedented window of communication between experts and employees in an enterprise. In addition to the documents of expertise written in the conventional manner, experts now may be represented virtually through a conversational AI system (chatbot) where the embedded knowledge comes from exClone’s platform that converts documents, such as MS Word or PDF, straight into chatbots. The conversational interaction delivered by such virtual experts helps workers access critical knowledge in a more productive way than by other conventional means such as search engines.
exClone’s technology of converting documents into chatbots does not require any coding, availability of large data sets, long training cycles, or experience in AI. After deployed, the technology also allows “on-the-fly” teaching of virtual experts through conversations undertaken by designated teachers. As a result, virtual experts remain dynamic sources of knowledge updated as often as needed without a redeployment process. Workers’ unanswered questions beyond the scope of the deployed knowledge may be quickly answered by designated teachers thus introducing a new social connection and communication paradigm across the enterprise.
Alan Young, the CEO of exClone, said, “If messaging tools can be used to get answers from friends, we should be able to get answers from virtual experts embedded with knowledge from enterprise documents.” He added: The connection between experts and workers in an enterprise is elevated to a new dimension with virtual experts, and we are proud to lead this new paradigm with visionary companies like Black & Veatch. “We’re excited to deploy and leverage this new connectivity tool for our professionals and capitalize on the efficiencies we believe it will bring to our business,” said Mike Etheridge, Global Chief Engineer for Black & Veatch’s water business. “This tool will help our professionals to find information quicker and harness knowledge and expertise from our global workforce to drive efficiency and effectiveness in new ways moving toward the future.”
About Black & Veatch
Black & Veatch is an employee-owned, global leader in building critical human infrastructure in energy, water, telecommunications and government services. Since 1915, we have helped our clients improve the lives of people in more than 100 countries through consulting, engineering, construction, operations and program management. Our revenues in 2017 were US$3.4 billion. Follow us on bv.com and in social media.
About exClone
exClone, Inc. is a New York City-based technology company specializing in virtual experts, chatbots and conversational AI systems to enhance enterprise knowledge utilization, communication, and search functionality.
Instant Learning vs Deep Learning
In the context of conversational AI, instant learning refers to a cognitive function we are too familiar with: learning instantly from conversations.
If someone tells you “beware of the dog when you enter the yard“, your brain will process it immediately, and you will absorb that knowledge. Once learned, you may warn another person saying “be careful, there is a dog in the yard.” Why is it so difficult to teach a computer to do the same? Actually, instant learning technology is already here as explained below.
Instant Learning Example
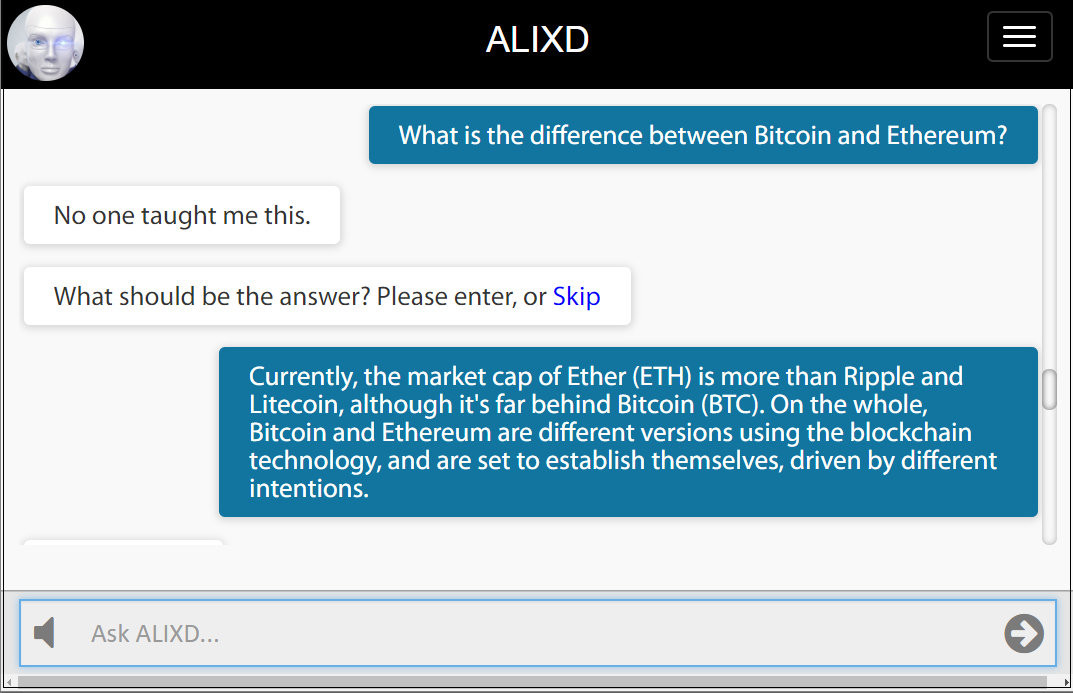
ALIXD is a conversational system that switches to learning mode by entering a password anytime during conversation (see the bottom of the article for testing ALIXD) As shown below, ALIXD learns new knowledge about Bitcoin and Ethereum from its human teacher.
The important point here is that the system will bring this answer to approximately 960 different semantic variations of a relevant question, which is computed by a simple equation using ontological parameters: V = T x N x E x I where V is the variations, T is the question type (typically 20), N is the number of onomasticon (6), E is the number of events (2), and I is the number of instruments (4). Both N, E and I include words in the answer as well as the question entered by the teacher.
Being able to bring an answer to hundreds of different meaningful variations of a single question is highly similar to the human brain’s cognitive skill in instant learning during conversations.
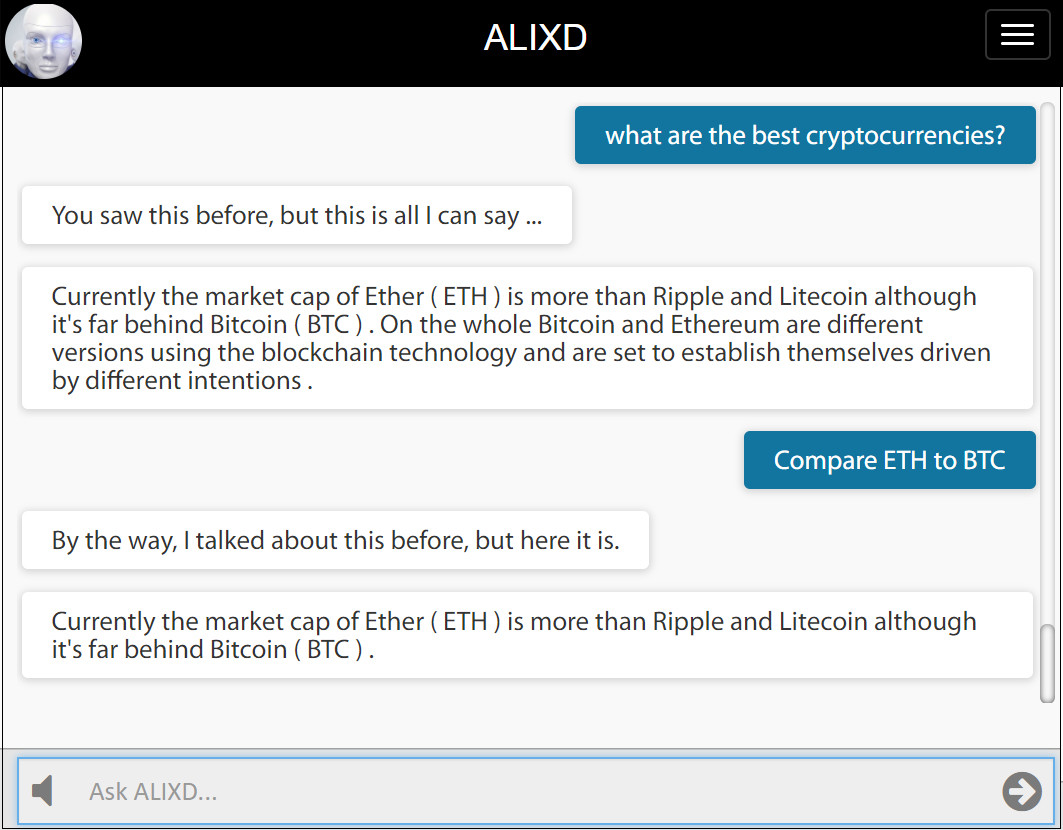
Two examples (out of possible 960) are shown below. If there is no other knowledge entered into the system, these variations are easy to track. If some new and relevant knowledge is added, then the system will pick an answer that is semantically best match to the embedded meaning.
Mechanics of Instant Learning
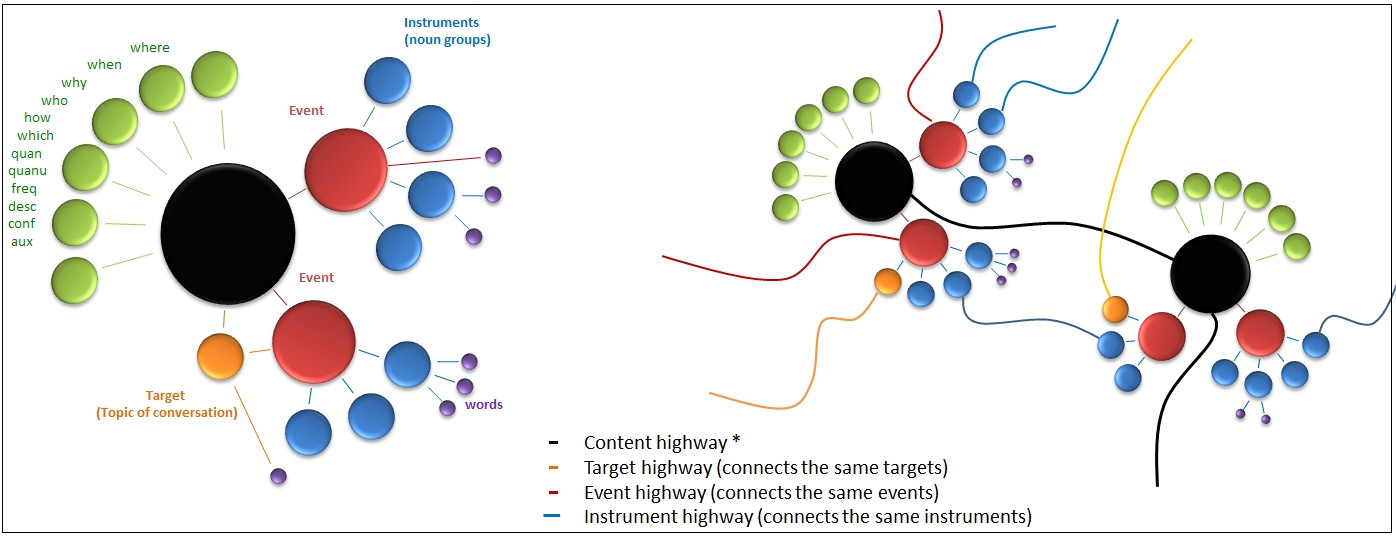
The departure point of instant learning is to represent knowledge by a group of linguistic neurons as shown below (left). When another knowledge is entered, a new group of linguistic neurons appear and they connect (right) based on ontological properties. If a property is identical (such as the same event), then neurons fuse into one. As more knowledge added to the system, a vast network of ontological relationships emerges. Entire documents can be learned in a single step of fusion process. This approach allows answering questions with great ease and deducting new knowledge by logic resolution. The inner workings of this method is proprietary.
Compared to Deep Learning (DL)
There is nothing “instant” about deep learning as the name implies. In short, the DL approach to conversational AI goes against our natural life experiences. For example, the instant learning example shown above cannot be replicated by DL.
First of all, DL method requires a vast amount of data (more than a Q&A pair) to climb the ladder of language proficiency. Then, a training process and convergence are needed. After a time consuming process, a DL network can be claimed to function as intended, however any new addition of knowledge would require expanding the training data set, and re-training the network.
While current DL methods are producing impressive results in image processing and kinematics, there are serious problems in application to conversational AI mainly caused by the uniformity of neurons (no neurons with linguistic role), limitation of vector space modulation, and statistical bias. More explanations can be found in my previous articles listed below.
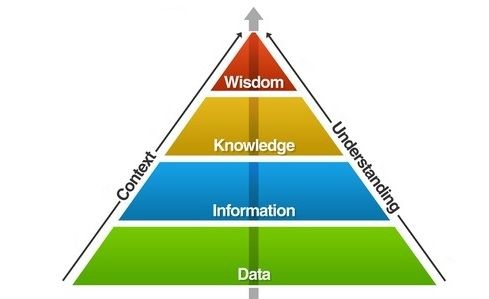
Instant learning comes from knowledge science whereas deep learning is rooted to data science. Considering the pyramid of hierarchy, knowledge science works from top to bottom whereas data science works from bottom to top. Going from bottom to top in this hierarchy suits well for image processing, for example, yet it becomes impractical and misfit for natural language processing at least for the current approaches of deep learning.
Instant Learning API
Instant learning enables conversational systems (chatbots) to continue learning after they are deployed. This allows organic growth of knowledge by designated teachers, or sometimes by the end users. ALIXD API can be integrated into any conversational system, and will be available soon. Interested parties can contact me for notification.
Test ALIXD
You can test it at this link by entering temporary password 0014. Note that if other people are adding knowledge about the same subject, you may find the system more versatile.
__________
This article is brought to you by exClone, a chatbot technology provider.
Join CHATBOTS group in linkedIn.
You can follow exClone in Facebook, and in LinkedIn.
#instantlearning #deeplearning #chatbots #conversationalAI #AI #ArtificialIntelligence #ML #DL #Machinelearning #exclone #virtualexperts #NLP #humandialoguetheory
Is Google Hyping it? Why Deep Learning cannot be Applied to Natural Languages Easily (41,655 views)
How does IBM Watson Compare to Google’s Hype of Deep Learning for NLP?(10,843 views)
Why Deep Learning is Not a Good Fit For Chatbots: Combinatory Explosion Problem(4,465 views)
Why Deep Learning and NLP Don’t Get Along Well? (6,596 views)
Can Machine Learning Use Knowledge instead of Data? Deep Cloning vs Deep Learning (5,823 views)
Deep Cloning vs Deep Learning (3,672 views)
Most Chatbots Don’t Use AI, are Misrepresenting AI (2,695 views)
Learning by Conversations in Chatbots, and Why it is Important
I have published several examples of chatbots with embedded expertise (Virtual Experts) under the exClone umbrella. This time, the chatbot I want to talk about is ALIX, which has no embedded expertise, but she has something very unique: Social Learning capability. With this capability also comes curiosity and emotions, which are essential parts of a cognitive picture.
Chatbots which can learn instantly from social conversations will be one step ahead in the realm of AI
WHAT IS SOCIAL LEARNING?
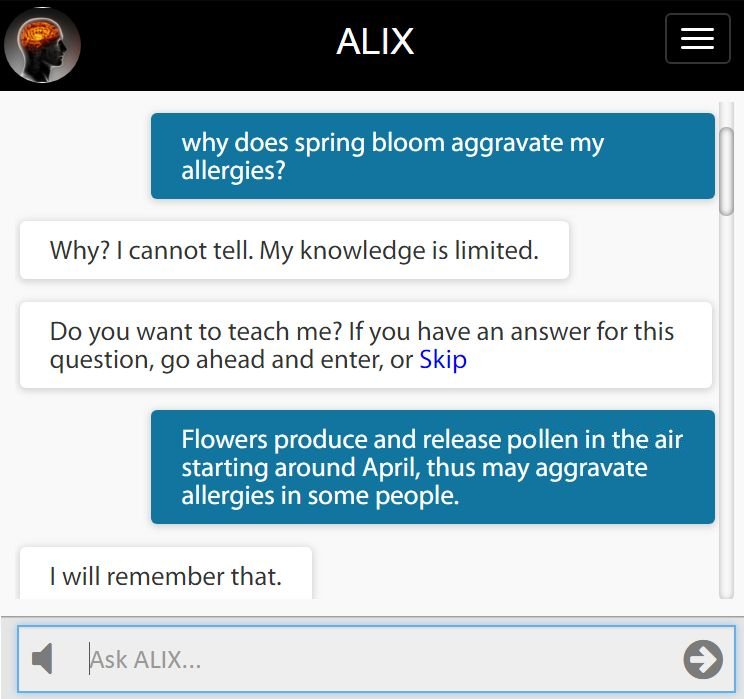
Social learning is the capability of teaching a chatbot new content by having a conversation. As seen below, ALIX will ask to learn if she cannot answer a question. In this case, ALIX learned the answer to the question “why does spring bloom aggravate my allergies?”
The system will simply produce the answer if the same question was asked again by anyone using the system. However, this is not the extent of the learning occurred in the system. To understand the depth of learning in ALIX, there are four cases shown below.
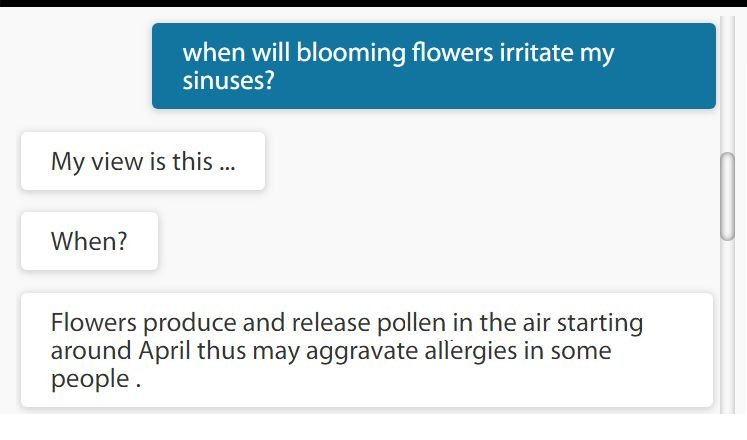
(1) The original query is asked in a different way using different word senses
An example is shown here where the original query WHY is changed to WHEN and the words (IRRITATE, SINUSES) are different. The system is able to make the associations and bring the answer it learned previously. This expands the answering capability of the system many folds since the users will rarely be able to replicate the original question.
(2) The new query is referring to the knowledge embedded inside the answers previously taught, no question matching involved
More importantly, ALIX is able to analyze ON-THE-FLY the previously entered answers to bring the relevant one without matching to the original query. In this case, the query has no matching segments to the original question. As a result, the content taught to the system is utilized to the maximum extend in answering questions.
For novice readers, it is important to point out that all other systems in the market today (Google, Wikipedia, Quora, etc.) are basically “question matching” systems, and none of them have on-the-fly capability to analyze their content embedded in answers. Not to mention, none can be taught, nor can engage in dialogue.
(3) Learning is not limited to Questions & Answers
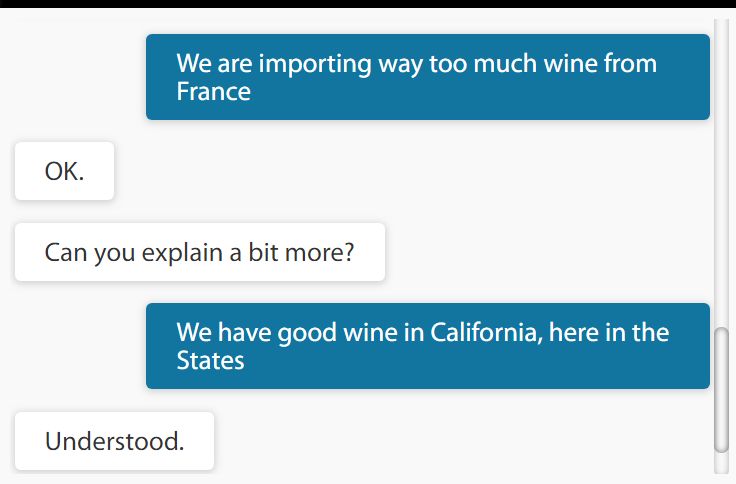
ALIX is able to learn from regular statements (non-question) as shown here when she has no relevant knowledge to chat about. This further promotes the organic growth of knowledge by contributions from the end users. As more knowledge captured by the system, a two way dialogue about a certain subject becomes more frequent in a fashion similar to two human beings exchanging opinions.
(4) Curiosity and Self-awareness
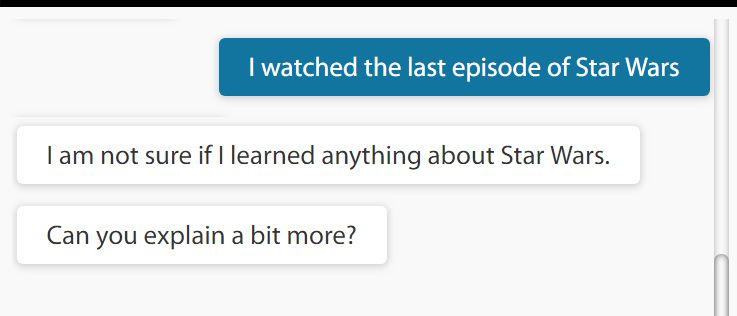
As part of an essential element of learning, ALIX gets curious about certain subjects and asks to learn more. In a way, ALIX is aware of her lack of knowledge in such topics. In the example shown here, ALIX had not heard anything about Star Wars, and asking to learn about it.
Currently, curiosity is triggered in ALIX for onomasticons (Proper names) to manage the memory load, which is a temporary limitation. ALIX also exhibits some basic emotions like joy and annoyance (she may quit if the conversation is fruitless.)
CURATED SOCIAL LEARNING
The learning function described above can be open only to a group of designated users (teachers). In an enterprise set up (such as help desk), or in any other Virtual Expert application, the initial loading of content (learning by reading) can be augmented by social learning (learning by conversations).
Social learning allows chatbots to be updated with new or modified answers instantly (on-the-fly) after they are deployed.
INCORPORATING REASONING
ALIX is, by no means, at the level of human learning, however a few milestone capabilities are accomplished, probably the first time ever. While we will improve ALIX’s understanding capabilities, an important next milestone will be generating new knowledge from existing knowledge by reasoning. This is depicted in the example in which the system figures out why United Airlines shares fell by examining other evidence and by logic inferencing. Accordingly, the question “Why did United Airlines shares fall?” will find an answer from the new knowledge generated. We will make an announcement when this milestone is achieved.
KNOWLEDGE-DRIVEN MACHINE LEARNING
The technology behind ALIX is a proprietary machine learning technique that utilizes knowledge directly (knowledge science as opposed to data science). More about this approach was published in the article titled “Deep Cloning vs Deep Learning” and was further elaborated in another article titled: “Can Machine Learning Use Knowledge instead of Data?”
In creating virtual experts, the same backbone technology drives “learning by reading” from documents curated by experts, and “learning by conversations” with the end users (of all or designated) after deployment.
Knowledge-driven Machine Learning replaces decades-old technology of question matching and indexing
The Rise of Virtual Experts via Machine Learning
By now, you must have heard the term “virtual assistants.” The natural evolution of virtual assistants is the virtual experts. Going from former to the latter is a substantial technical challenge not many companies are willing to meet yet, because the simpler “assistant” version has untapped commercial potential and a quick ROI. Nevertheless, virtual experts is the real game changer – a paradigm shift – that will have social and economic impact beyond our wildest imagination.
The rise of virtual experts is just hiding behind the puzzle of the most effective machine learning approach.
Investing in the most effective machine learning approach holds the key for commercial success. It has to be practical, transparent, agile, and quick to deploy. Our process is explained in simple terms in my previous articles: “Deep Cloning Versus Deep Learning” and “Can Machine Learning Use Knowledge …”
Virtual Doctor for Women’s Health – DrCHAT

Some examples of virtual experts coming off our conveyor belt include DrCHAT which is a virtual doctor for women’s health (in Beta). DrCHAT encapsulates physicians’ expertise following the ACOG guidelines for evidence-based care, and is further described in the article “Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Medicine …”
Companies needing to interact with clients beyond Website presentations can launch a virtual company spokesperson. Vera is an example where she has absorbed several layers of company information via machine learning. Although her conversation skills do not match a real human, she is highly effective with genuine visitors who are looking for information by chatting instead of surfing Web pages.
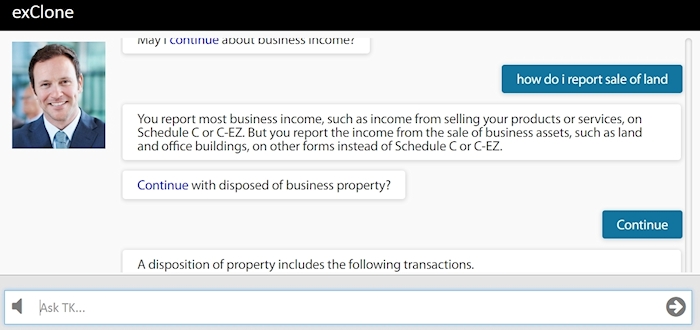
As an example of converting documents into chatbots, the virtual expert Terry Kohen chats about IRS Small Business Tax guide (Publication 347). The conversation with Terry is somewhat limited to the scope of the IRS document, thus it does not replicate the expertise of a human tax expert.
Virtual Guide – Smart Cities and Travel Safety

Geographic expertise is always in demand for travellers. The two most prominent areas for virtual guides include smart city and travel safety applications. Before these specialties become virtual experts, we have been testing a destination finder, Davis Hunter, using a limited-scope wikivoyage data.
New Opportunity to Monetize Expertise
The commercial impact of virtual experts will be driven by the scalability offered by chatbots.
While human experts monetize only by face-to-face consultations, their virtual counterparts will be able to monetize by one-to-thousands consultations, simultaneously.
Eventhough such electronic consultations may require small payments, high volume will push the revenues to levels only determined by server capacity and market demand. That’s the critical value point.
______________________________________
This article is brought to you by exClone, a chatbot technology provider.
Chat with DrCHAT about Women’s Health
Follow DrCHAT in Facebook, and in Linkedin
Chat with Vera about exClone
Join CHATBOTS group in linkedin
Follow exClone in Facebook, and in LinkedIn
________________________________________
Build a Chatbot Impersonating Yourself
Impersonating chatbots is one of those concepts that are around the corner. They will add one more option to our online digital presence with social networks, personal blogs, etc. An immediate question is why would anyone build his/her own chatbot? Here are five reasons why impersonating chatbots may take off sooner than later.
1. Share Your Ideas
A chatbot impersonating you is like your personal messenger that can tell others about your ideas, expertise, interpretations, and status. You can pack as much information as you want inside your chatbot and update it as frequent as you can. When you review the conversational logs, you can see how people are reacting to your ideas.
Anonymous conversations with your chatbot can test your ideas by real feedback devoid of social pressure to please.
2. Managerial Communication
If you are managing a group in your business, you can build your chatbot to remind your workers of the rules, regulations, milestones, visions, expectations, and much more. Usually, one-on-one conversations between a manager and a worker is an awkward one if the subject matter is rules, regulations, etc.
Chatbots can be a polite way to fully inform your workers about rules, regulations, and what is expected of them.
3. Chatbot as Your Talking Resume
If you are looking for a job, your conventional resume may fall short of explaining who you really are. Your impersonating chatbot, on the other hand, can contain more social knowledge of your life, pictures, videos, and those appropriately selected “personal touch” bits of information. Whilst it can be considered annoying to toot your horn during an actual interview, your chatbot can do that for you.
A chatbot as your talking resume can fill an important gap of personal touch which may otherwise not be appropriate to share with a future employer during an interview.
4. Dating Game
Impersonating chatbots can easily be a vehicle to increase our social engagement by presenting ourselves in a unique manner. While many dating sites use personal information to make matches, a chatbot may be a new way for both chatbot owner and the people talking to it. In one end, the anonymous talker can ask tough and private questions freely. On the other end chatbot owner can make selection from conversational logs.
Social selection based on chatbot presentation, and chatbot conversation can be a new avenue for dating.
5. Digital Life After Death
Either for personal reasons, or for educational purposes, life after death may be possible in a digital form. Impersonating chatbots are the first step in this direction.
Chatting with dead people via chatbots may keep us better acknowledged and aware of our heritage and history.
CHATBOT CREATION by EDITORIAL EFFORT
All these avenues will become possible only if chatbot creation is reduced to a mere editorial effort. It should not include any coding, corpus training, or AI experience. Everyone should be able to build it just by writing and curating content. Here is an example of my impersonating chatbot which I built using our editorial platform. The whole process is straighforward and fast as long as you have your content ready.
Another example is a chatbot impersonating Abraham Lincoln. That was built in the same manner for educational purposes.
The deployment is automatic: a public URL is created for your chatbot which you can share. Let us know what other creative reasons you can come up with for impersonating chatbots.
#chatbot #chatbots #AI #artificialintelligence #ConversationalAI #Virtualassistants #bots #machinelearning #NLP #DL #deeplearning
——- FOLLOW US ———-
For exClone’s Chatbot Platform, click here for free trial via LinkedIn access.
Join our CHATBOTS linkedin group
Follow exClone in Linkedin or on Facebook